How to Protect Your Azure App Service App from DDoS Attacks

Azure App Service is a PaaS offering and its components, including Azure VMs, storage, network connections, web frameworks, management and integration features, are actively secured and hardened. It has a basic level of DDoS protection.
However, this basic layer of protection can be limited when facing large-scale attacks.
What is DDoS#
Distributed denial of Service (DDoS) is a common attack towards a web application to exhaust its resources with a flood of traffic. As a result, the web application will exhibit as unavaiable to it legitmate users.
You can identify a DDoS attack with the below features[1]:
- Suspicious amounts of traffic originating from a single IP address or IP range
- A flood of traffic from users who share a single behavioral profile, such as device type, geolocation, or web browser version
- An unexplained surge in requests to a single page or endpoint
- Odd traffic patterns such as spikes at odd hours of the day or patterns that appear to be unnatural (e.g. a spike every 10 minutes)
Dynamic IP Restriction#
If you are using App Service Windows, you can make use of Dynamic IP Restriction(DIPR) feature of IIS(Internet Information Service) webserver. You can add an extension from Azure Portal called Dynamic IP Restriction for App Services. With this extension, you can define blocking rules on IPs based on their accessing patterns.
- The number of concurrent requests made.
- The number of requests made in certain interval of time.
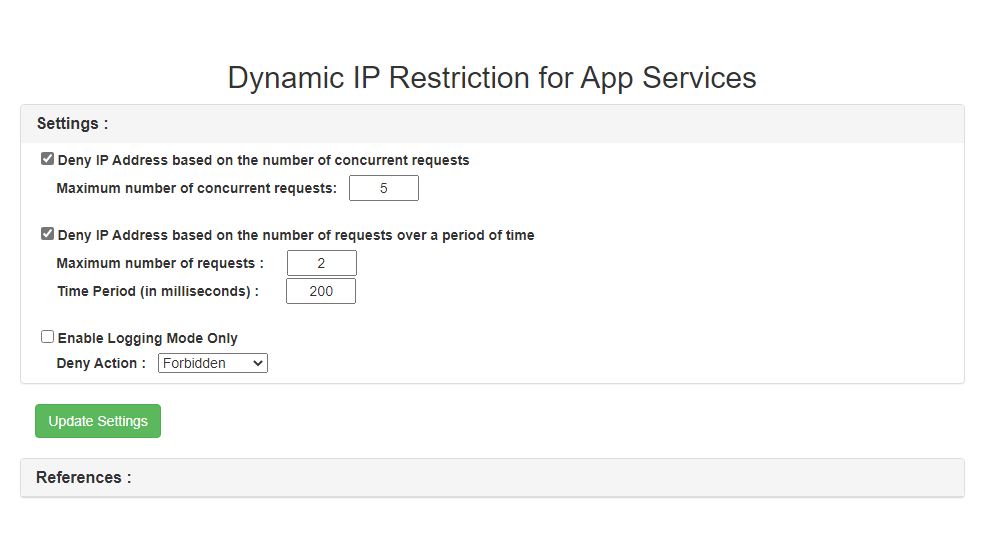
This extension will create special configuration file applicationHost.xdt in C:\home\site based on your customized rules. For more information about the usage of this extension, please refer to Dynamic IP Restriction for App Services.
Azure DDoS Protection Standard#
Another option is to purchase an Azure DDoS Standard plan and configure it with Application Gateway WAF or Azure Front Door WAF. It is worth mentioning that Azure DDoS Protection Standard(Metwork) only has a fixed monthly bill of $2,944 (as of October 2022). There is also a IP Protection plan will be in public preview soon.
To use this service, your App Service app needs to be behind of a WAF enable load balancing service like Application Gateway.
Integrate Azure App Service app with Application Gateway#
First of all, we need to create a Application Gateway with WAF enabled Quickstart: Direct web traffic with Azure Application Gateway - Azure portal. To integrare the Application Gateway with App Service, there two options.
- The first option makes use of a custom domain on both [Application Gateway and the App Service in the backend][3].
- The second option is to have Application Gateway access App Service using its default domain, suffixed as ".azurewebsites.net".
Generally, we all have a custom domain mapped to our App Service app, so we choose the first option.
DNS Configuration#
In terms of the DNS settings, we need to add a CNAME or A record at the DNS provider and map our custom domain to the Application Gateway (Default Domain or Public IP address.) If you would like to use a CNAME record, you need to go to the App GW Public IP on Azure Portal and set up a DNS name lable for this IP. After which, your IP will has a name like yourcustomname.region.cloudapp.azure.com. 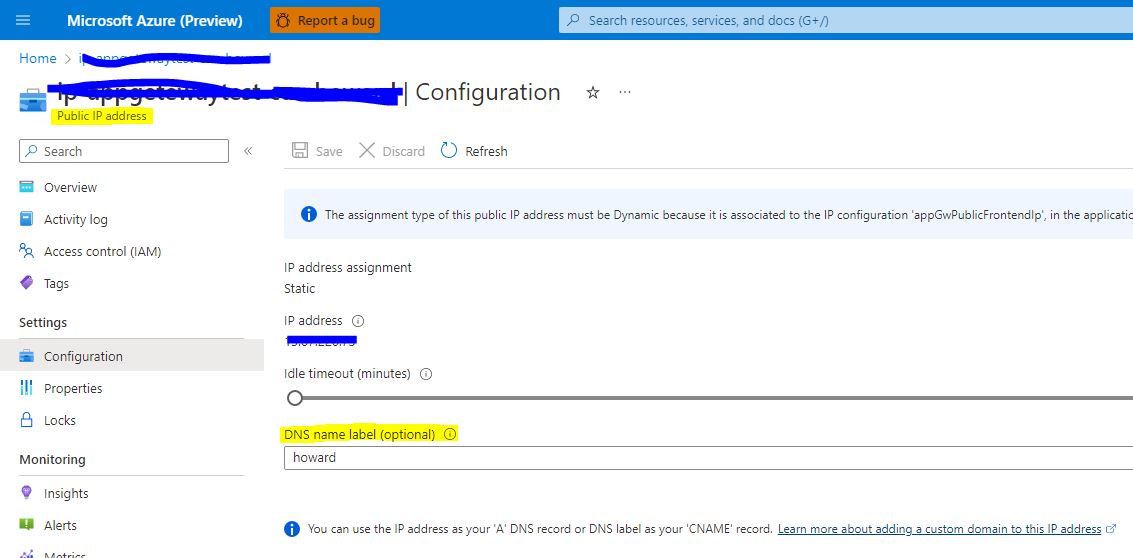
If you have configured the custom domain directly for your App Service before, remeber to remove your old DNS records. The DNS configuration for the custom domain will be directed towards Application Gateway.
TLS bindings#
Because we need to use the certificate at both App Service side and the Application Gateway side, the free App Service managed certificate would not meet the needs. You need to purchase a certificate for your custom domain and generate a PFX version for the later usage. After acquiring the PFX version of the certificate, upload it to Azure App Service at Azure Portal >> TLS/SSL settings >> Private Key Certificates (.pfx) >> Upload Certificate. If you purchased your certificate from App Service, you can choose Import App Service Certificate, dowload the certificate from KeyVault and generate a PFX version. You can follow this tutorial to achieve this.
Configure your Application Gateway#
Now we need to configure your Application gateway. We need to create a backend pool and set our App Service as the backend target. After which, we need to create an HTTPS Backend setting and be sure to choose No for Override with new host name. You shoule also create a Custom probe and use your custom domain as the Host and the HTTPS settings we just created.
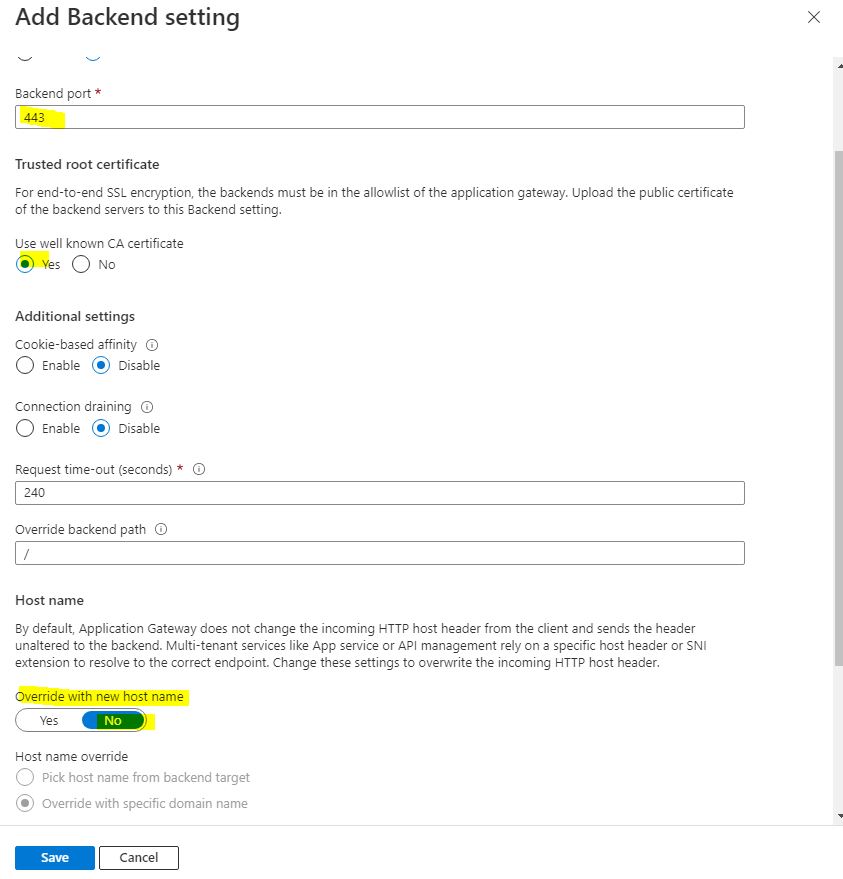
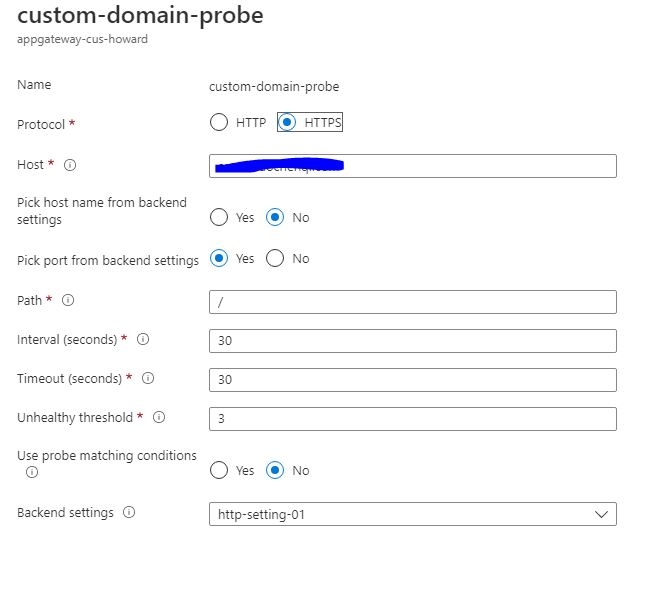
The we need to create a listener and upload the PFX certificate you created in the last step and write your custom domain in Host name. After configuring the listener, create a new rule to connect the listener and the backend pool.
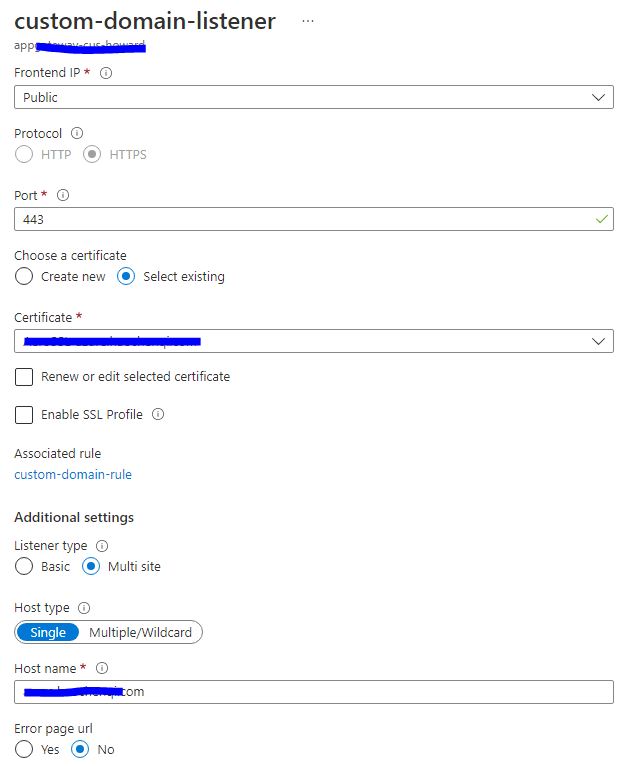
If you have configured the Application Geteway properly, now when you visit your app with the custom domain, you should be using the Application Gateway. You can now go to the Access Restriction of your App and only allow the traffic from the subnet of the virtual network(VNET) where your Application Gateway resides in.
Enable the DDoS Protection#
The Last steps is to create a DDoS Protection plan and enable DDoS protection for the VNET where your Application gateway is. Please refer to the Quickstart: Create and configure Azure DDoS Network Protection using the Azure portal for detailed steps.
Summary#
In this article, we have learned two ways on how to protect your App Service apps from DDoS sttacks. The first one is using Dynamic IP restriction and the second one is to leverage Azure DDoS Protection Plan.
Reference:
[1] https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/ddos/what-is-a-ddos-attack/
[2] https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/overview-security
[3] https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/application-gateway/configure-web-app?tabs=customdomain%2Cazure-portal