How to Upload Files to AWS S3 in Node.js?

Amazon Simple Storage Service is storage for the Internet. It is designed to make web-scale computing easier for developers. -- Amazon
Simple Storage Service(S3) is a an object storage service provided by AWS in 2006. S3 provides developers with a distributed data storage service with high scalability, high durability and high availability. The data storage structure of S3 is very simple, which is a flat two-layer structure: one layer is a bucket, and the other layer is a storage object. A bucket is a way to classify data in S3, it is a container for data storage and every object needs to be stored in a certain bucket. It will become a part of the domain name for users to access data, so the name of the bucket must be unique.
Our Node Apps often need to store user data like images, audio files, documents ,etc into somewhere secure and easily accessible instead of on local server. This is when S3 comes in as a perfect option. In this blog, we will go through how to upload your files in AWS s3 buckets.
Create a S3 Bucket#
In this section, we will create a bucket on S3 for us to upload files in. To get start, you need to generate AWS Security Key Access Credentials first from your AWS Management console.
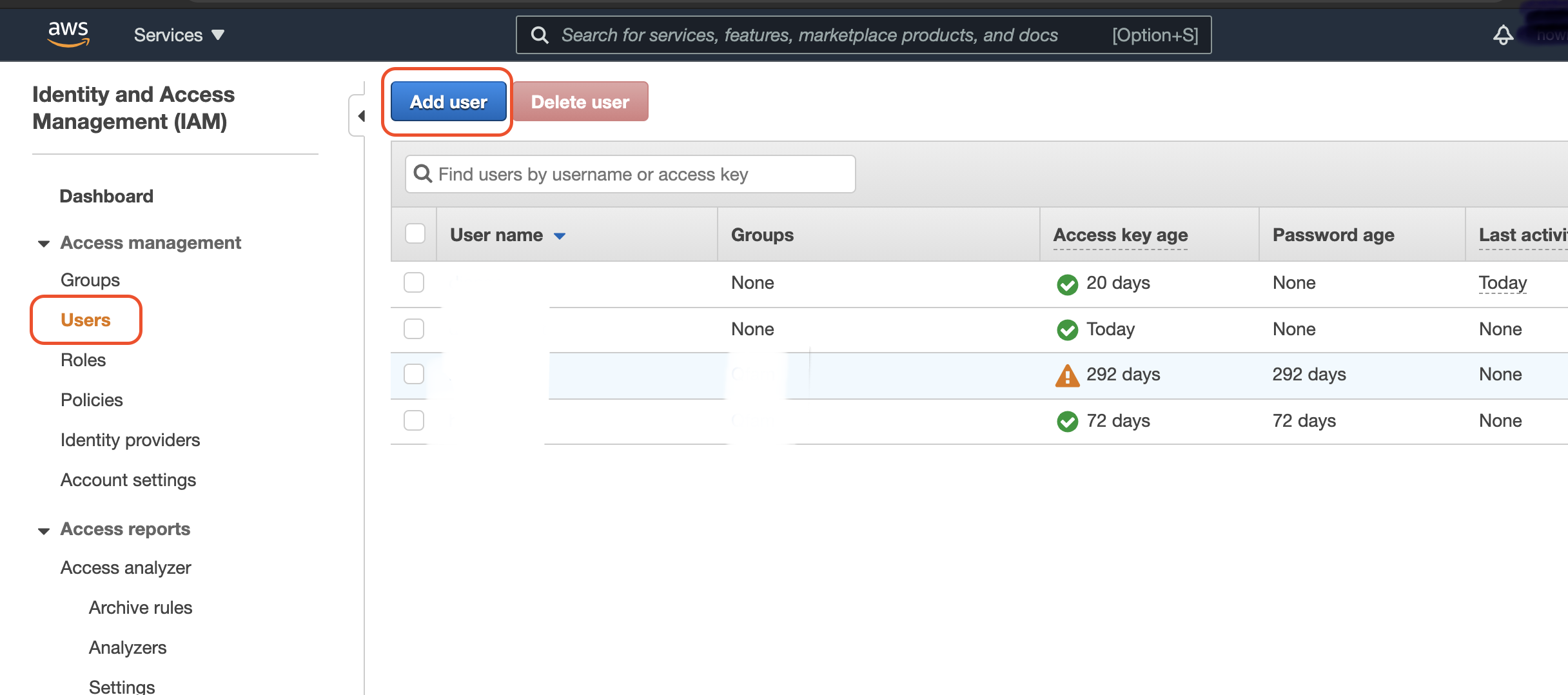
On the AWS Services panel, find IAM and click to go IAM dashboard. Under the Access Management section, find Users >> Add User.
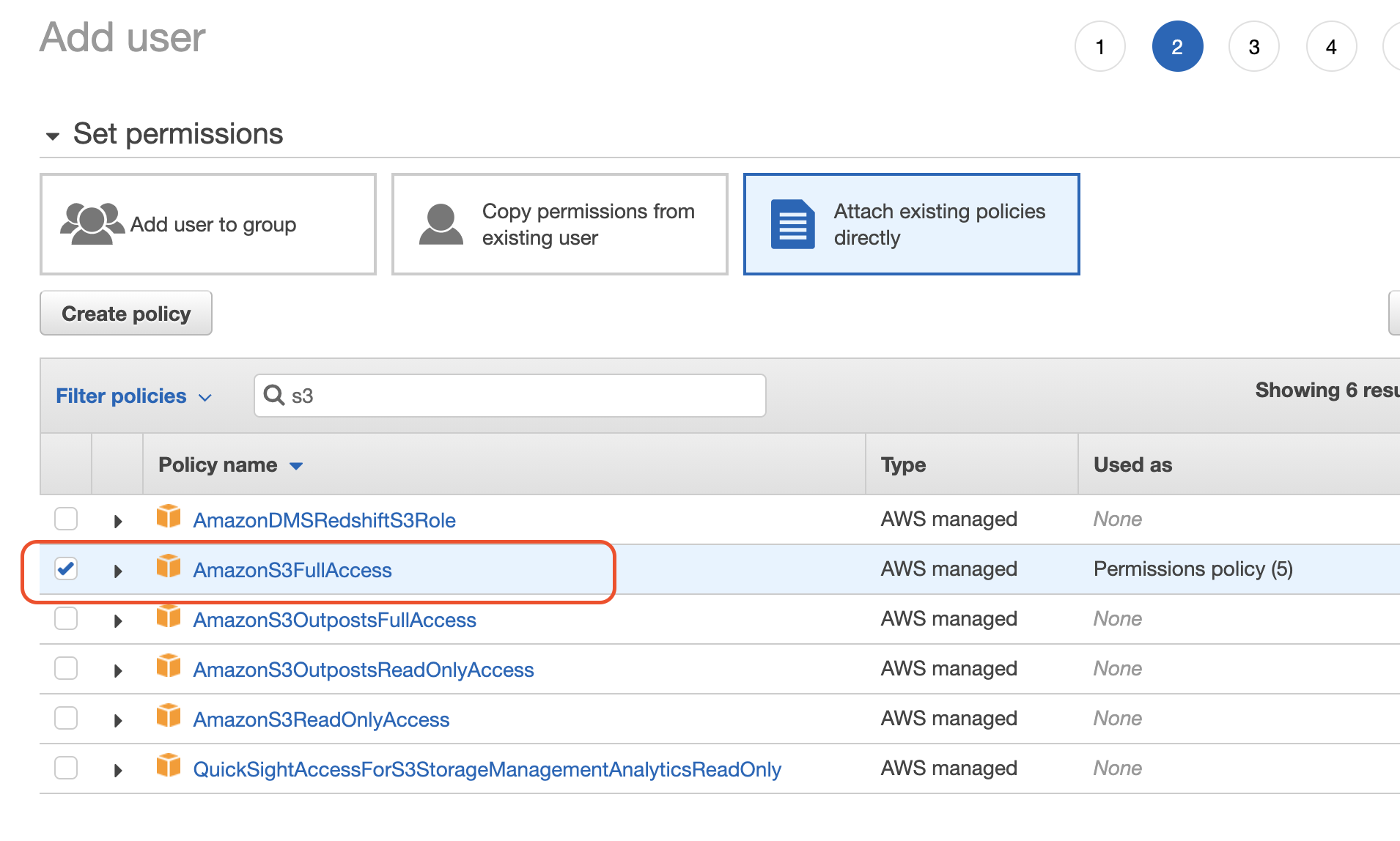
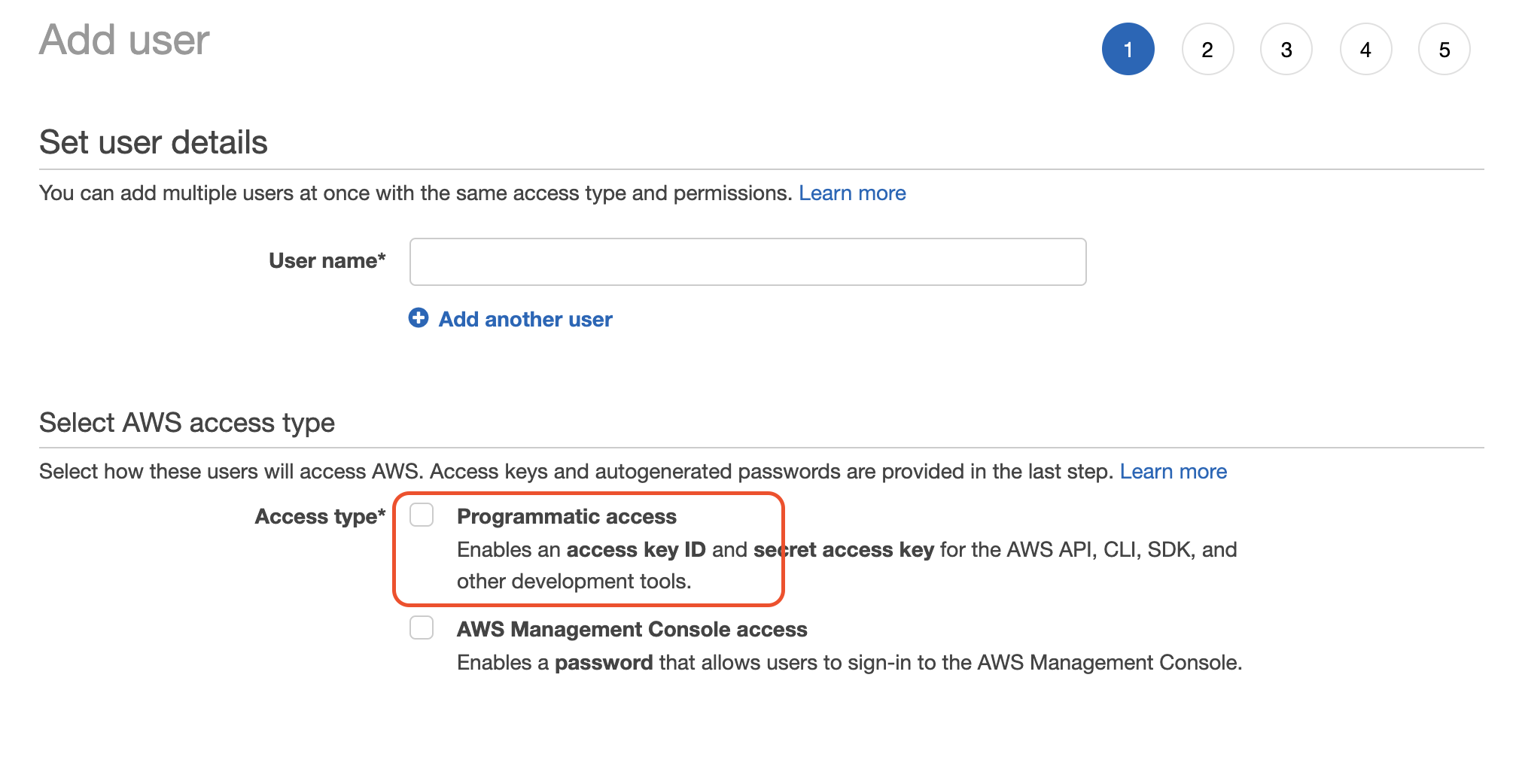 Then follow the steps to create a programmatic access AWS user attached with AmazonS3FullAccess policy. Save your access key ID and secret access key in a secure place as you won't able to check them again.
Then follow the steps to create a programmatic access AWS user attached with AmazonS3FullAccess policy. Save your access key ID and secret access key in a secure place as you won't able to check them again.
Now let us create a bucket with a unique name. Similarly, find S3 On the AWS Services pane. On the dashboard, click Create bucket to create a new bucket with proper region and other default settings. After you create a bucket, we need to allow our client application to interact with our bucket. Go to Your Bucket >> Permissions >> Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS). Change the configuration as bellow.
[ { "AllowedHeaders": ["*"], "AllowedMethods": ["POST", "GET", "PUT", "DELETE", "HEAD"], "AllowedOrigins": ["*"], "ExposeHeaders": [] }]Now, We have a bucket up for us to play with. Alternatively, you can also create a bucket with AWS SDK tool. Simply felllow here.
Create a Simple Node App#
Now let us interact with our created bucket. Before we create a S3 instance, make sure to put sensitive data in the environment variables, simply create a .env file and save your data in that file. Here I will use a library called dotenv to handle .env file, it will loads environment variables from a .env file into process.env.
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=Your AWS Access Key IDAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=Your AWS Secret Access KeyS3_BUCKET=Your Bucket NameThen let's create a S3 instance after we install all necessary dependencies with:
$ npm i dotenv aws-sdkCreate a file name with app.js, let's write code in this file.
require("dotenv").config();
const fs = require("fs");const AWS = require("aws-sdk");
const s3 = new AWS.S3({ accessKeyId: process.env.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, secretAccessKey: process.env.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY,});Interact With Our Bucket#
With the S3 instance set up, we can now play with our bucket. We can upload files to our bucket, get all the files in our bucket and delete files. Before we upload the file, we need to read its contents in a buffer. After reading it, we can define the needed parameters for the file upload, such as Bucket, Key, and Body.Let's see the code.
/** * Upload files **/const uploadToS3 = async (file) => { // Read content from the file const fileContent = fs.readFileSync(file);
// Setting up S3 upload parameters const params = { Bucket: process.env.S3_BUCKET, Key: "your_image.jpg", // File name you want to save as in S3 Body: fileContent, };
// Uploading files to the bucket s3.upload(params, function (err, data) { if (err) { throw err; } console.log(`File uploaded successfully. ${data.Location}`); });};uploadToS3("your_image.jpg");If you want to list all objects in your bucket, you can use S3 listObjectsV2 function.
/** * List all objects in the bucket */getlist = async () => { const params = { Bucket: process.env.S3_BUCKET, Delimiter: "", }; try { const response = await s3.listObjectsV2(params).promise(); this.setState({ list: response.Contents, fetched: true, }); console.log(this.state.list); } catch (err) { this.setState({ ifError: true, errorCode: err.code, }); console.log("S3 ERROR : " + err.code); }};consloe.log(getlist());Now run your js file to see the result.
$node app.jsConclusion#
In this blog, we created simple Node App and interact with our bucket. Nowadays, using a cloud storage service like AWS S3 is a very popular way to reduce storage pressure for servers as well as securly store user data.
Reference: AWS S3 Doc